Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
2.6.8.21. Segmentation with Gaussian mixture models¶
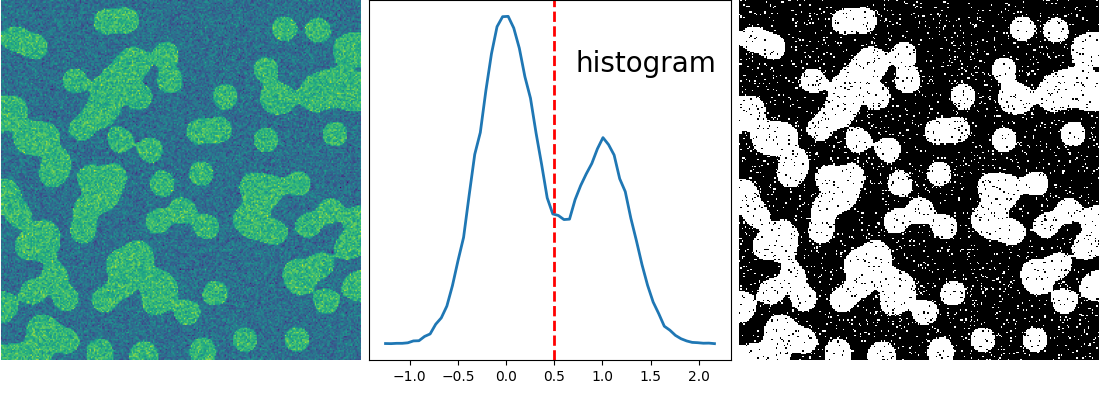
This example performs a Gaussian mixture model analysis of the image histogram to find the right thresholds for separating foreground from background.
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixture
rng = np.random.default_rng(27446968)
n = 10
l = 256
im = np.zeros((l, l))
points = l * rng.random((2, n**2))
im[(points[0]).astype(int), (points[1]).astype(int)] = 1
im = sp.ndimage.gaussian_filter(im, sigma=l / (4.0 * n))
mask = (im > im.mean()).astype(float)
img = mask + 0.3 * rng.normal(size=mask.shape)
hist, bin_edges = np.histogram(img, bins=60)
bin_centers = 0.5 * (bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:])
classif = GaussianMixture(n_components=2)
classif.fit(img.reshape((img.size, 1)))
threshold = np.mean(classif.means_)
binary_img = img > threshold
plt.figure(figsize=(11, 4))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(132)
plt.plot(bin_centers, hist, lw=2)
plt.axvline(0.5, color="r", ls="--", lw=2)
plt.text(0.57, 0.8, "histogram", fontsize=20, transform=plt.gca().transAxes)
plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(133)
plt.imshow(binary_img, cmap="gray", interpolation="nearest")
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.02, hspace=0.3, top=1, bottom=0.1, left=0, right=1)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.736 seconds)