Scipy sparse arrays#
Section author: Robert Cimrman
(Dense) matrix is:
mathematical object
data structure for storing a 2D array of values
Important features:
memory allocated once for all items
usually a contiguous chunk, think NumPy ndarray
fast access to individual items (*)
Why Sparse Matrices?#
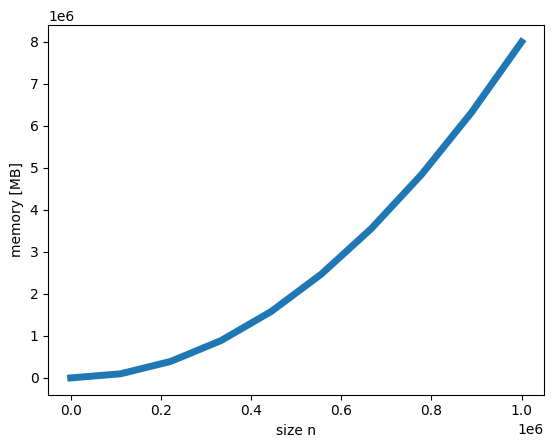
the memory grows like
n**2for dense matrixsmall example (double precision matrix):
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0, 1e6, 10)
plt.plot(x, 8.0 * (x**2) / 1e6, lw=5)
plt.xlabel('size n')
plt.ylabel('memory [MB]')
Text(0, 0.5, 'memory [MB]')
Sparse Matrices vs. Sparse Matrix Storage Schemes#
sparse matrix is a matrix, which is almost empty
storing all the zeros is wasteful -> store only nonzero items
think compression
pros: huge memory savings
cons: slow access to individual items, but it depends on actual storage scheme.
Typical Applications#
solution of partial differential equations (PDEs)
the finite element method
mechanical engineering, electrotechnics, physics, …
graph theory
nonzero at
(i, j)means that nodeiis connected to nodej
natural language processing
nonzero at
(i, j)means that the documenticontains the wordj
…
Prerequisites
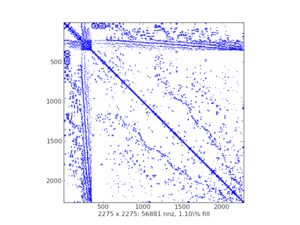
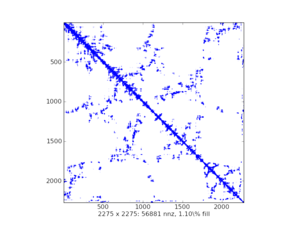
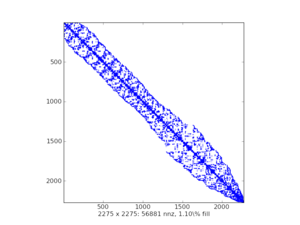
Sparsity Structure Visualization#
spy()frommatplotlibexample plots: