Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
2.7.4.6. Optimization with constraints¶
An example showing how to do optimization with general constraints using SLSQP and cobyla.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy as sp
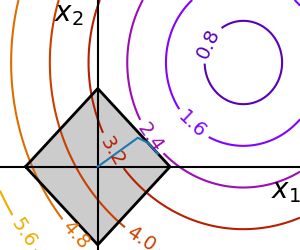
x, y = np.mgrid[-2.03:4.2:0.04, -1.6:3.2:0.04] # type: ignore[misc]
x = x.T
y = y.T
plt.figure(1, figsize=(3, 2.5))
plt.clf()
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1))
contours = plt.contour(
np.sqrt((x - 3) ** 2 + (y - 2) ** 2),
extent=[-2.03, 4.2, -1.6, 3.2],
cmap="gnuplot",
)
plt.clabel(contours, inline=1, fmt="%1.1f", fontsize=14)
plt.plot([-1.5, 0, 1.5, 0, -1.5], [0, 1.5, 0, -1.5, 0], "k", linewidth=2)
plt.fill_between([-1.5, 0, 1.5], [0, -1.5, 0], [0, 1.5, 0], color=".8")
plt.axvline(0, color="k")
plt.axhline(0, color="k")
plt.text(-0.9, 2.8, "$x_2$", size=20)
plt.text(3.6, -0.6, "$x_1$", size=20)
plt.axis("tight")
plt.axis("off")
# And now plot the optimization path
accumulator = []
def f(x):
# Store the list of function calls
accumulator.append(x)
return np.sqrt((x[0] - 3) ** 2 + (x[1] - 2) ** 2)
def constraint(x):
return np.atleast_1d(1.5 - np.sum(np.abs(x)))
sp.optimize.minimize(
f, np.array([0, 0]), method="SLSQP", constraints={"fun": constraint, "type": "ineq"}
)
accumulated = np.array(accumulator)
plt.plot(accumulated[:, 0], accumulated[:, 1])
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.048 seconds)