Generate figures for quick reference tables#
This final section contains the code for figures used in the line properties table in the Matplotlib page.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Machinery to store outputs for later use.
# This is for rendering in the Jupyter Book version of these pages.
from myst_nb import glue
Line property figures#
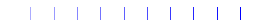
This example demonstrates using alpha for transparency:
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0.1, 1, 0.8), frameon=False)
for i in range(1, 11):
plt.axvline(i, linewidth=1, color="blue", alpha=0.25 + 0.75 * i / 10.0)
plt.xlim(0, 11)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_alpha", fig, display=False)
This example demonstrates aliased versus anti-aliased text.
First, aliased text (antialiased=False):
size = 128, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1), frameon=False)
plt.rcParams["text.antialiased"] = False
plt.text(0.5, 0.5, "Aliased", ha="center", va="center")
plt.xlim(0, 1)
plt.ylim(0, 1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Reset rcParams back to defaults
plt.rcdefaults()
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_aliased", fig, display=False)
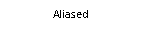
Next, antialiased=True.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1), frameon=False)
plt.rcParams["text.antialiased"] = True
plt.text(0.5, 0.5, "Anti-aliased", ha="center", va="center")
plt.xlim(0, 1)
plt.ylim(0, 1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Reset rcParams back to defaults
plt.rcdefaults()
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_antialiased", fig, display=False)

An example demoing the various colors taken by Matplotlib’s plot.
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0.1, 1, 0.8), frameon=False)
for i in range(1, 11):
plt.plot([i, i], [0, 1], lw=1.5)
plt.xlim(0, 11)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([]);
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_color", fig, display=False)
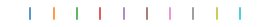
Plot various linewidths with Matplotlib.
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0.1, 1, 0.8), frameon=False)
for i in range(1, 11):
plt.plot([i, i], [0, 1], color="b", lw=i / 2.0)
plt.xlim(0, 11)
plt.ylim(0, 1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([]);
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_linewidth", fig, display=False)
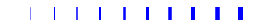
An example demoing the solid cap style in Matplotlib.
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1), frameon=False)
plt.plot(np.arange(4), np.ones(4), color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_capstyle="butt")
plt.plot(
5 + np.arange(4), np.ones(4), color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_capstyle="round"
)
plt.plot(
10 + np.arange(4),
np.ones(4),
color="blue",
linewidth=8,
solid_capstyle="projecting",
)
plt.xlim(0, 14)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([]);
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_solid_capstyle", fig, display=False)

An example showing the different solid joint styles in Matplotlib.
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1), frameon=False)
plt.plot(np.arange(3), [0, 1, 0], color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_joinstyle="miter")
plt.plot(
4 + np.arange(3), [0, 1, 0], color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_joinstyle="bevel"
)
plt.plot(
8 + np.arange(3), [0, 1, 0], color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_joinstyle="round"
)
plt.xlim(0, 12)
plt.ylim(-1, 2)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_solid_joinstyle", fig, display=False)
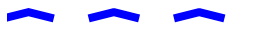
An example demoing the dash capstyle.
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1), frameon=False)
plt.plot(
np.arange(4),
np.ones(4),
color="blue",
dashes=[15, 15],
linewidth=8,
dash_capstyle="butt",
)
plt.plot(
5 + np.arange(4),
np.ones(4),
color="blue",
dashes=[15, 15],
linewidth=8,
dash_capstyle="round",
)
plt.plot(
10 + np.arange(4),
np.ones(4),
color="blue",
dashes=[15, 15],
linewidth=8,
dash_capstyle="projecting",
)
plt.xlim(0, 14)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_dash_capstyle", fig, display=False)

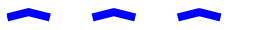
Example demoing the dash join style.
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1), frameon=False)
plt.plot(
np.arange(3),
[0, 1, 0],
color="blue",
dashes=[12, 5],
linewidth=8,
dash_joinstyle="miter",
)
plt.plot(
4 + np.arange(3),
[0, 1, 0],
color="blue",
dashes=[12, 5],
linewidth=8,
dash_joinstyle="bevel",
)
plt.plot(
8 + np.arange(3),
[0, 1, 0],
color="blue",
dashes=[12, 5],
linewidth=8,
dash_joinstyle="round",
)
plt.xlim(0, 12)
plt.ylim(-1, 2)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([]);
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_dash_joinstyle", fig, display=False)
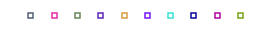
Demo the marker edge widths of Matplotlib’s markers.
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1), frameon=False)
for i in range(1, 11):
plt.plot(
[
i,
],
[
1,
],
"s",
markersize=5,
markeredgewidth=1 + i / 10.0,
markeredgecolor="k",
markerfacecolor="w",
)
plt.xlim(0, 11)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_mew", fig, display=False)

Demo the marker edge color of Matplotlib’s markers.
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1), frameon=False)
rng = np.random.default_rng()
for i in range(1, 11):
r, g, b = np.random.uniform(0, 1, 3)
plt.plot(
[
i,
],
[
1,
],
"s",
markersize=5,
markerfacecolor="w",
markeredgewidth=1.5,
markeredgecolor=(r, g, b, 1),
)
plt.xlim(0, 11)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_mec", fig, display=False)
Demo the marker face color of Matplotlib’s markers.
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1), frameon=False)
rng = np.random.default_rng()
for i in range(1, 11):
r, g, b = np.random.uniform(0, 1, 3)
plt.plot(
[
i,
],
[
1,
],
"s",
markersize=8,
markerfacecolor=(r, g, b, 1),
markeredgewidth=0.1,
markeredgecolor=(0, 0, 0, 0.5),
)
plt.xlim(0, 11)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_mfc", fig, display=False)

Demo the marker size control in Matplotlib.
size = 256, 16
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
plt.axes((0, 0, 1, 1), frameon=False)
for i in range(1, 11):
plt.plot(
[
i,
],
[
1,
],
"s",
markersize=i,
markerfacecolor="w",
markeredgewidth=0.5,
markeredgecolor="k",
)
plt.xlim(0, 11)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Store figure for use in reference table.
glue("plot_ms", fig, display=False)

Line styles figure#
def linestyle(ls, i):
X = i * 0.5 * np.ones(11)
Y = np.arange(11)
plt.plot(
X,
Y,
ls,
color=(0.0, 0.0, 1, 1),
lw=3,
ms=8,
mfc=(0.75, 0.75, 1, 1),
mec=(0, 0, 1, 1),
)
plt.text(0.5 * i, 10.25, ls, rotation=90, fontsize=15, va="bottom")
linestyles = [
"-",
"--",
":",
"-.",
".",
",",
"o",
"^",
"v",
"<",
">",
"s",
"+",
"x",
"d",
"1",
"2",
"3",
"4",
"h",
"p",
"|",
"_",
"D",
"H",
]
n_lines = len(linestyles)
size = 20 * n_lines, 300
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
plt.axes((0, 0.01, 1, 0.9), frameon=False)
for i, ls in enumerate(linestyles):
linestyle(ls, i)
plt.xlim(-0.2, 0.2 + 0.5 * n_lines)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Store figure for use in reference sections.
glue("line_styles_fig", fig, display=False)

Marker style figure#
def marker(m, i):
X = i * 0.5 * np.ones(11)
Y = np.arange(11)
plt.plot(X, Y, lw=1, marker=m, ms=10, mfc=(0.75, 0.75, 1, 1), mec=(0, 0, 1, 1))
plt.text(0.5 * i, 10.25, repr(m), rotation=90, fontsize=15, va="bottom")
markers = [
0,
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
"o",
"h",
"_",
"1",
"2",
"3",
"4",
"8",
"p",
"^",
"v",
"<",
">",
"|",
"d",
",",
"+",
"s",
"*",
"|",
"x",
"D",
"H",
".",
]
n_markers = len(markers)
size = 20 * n_markers, 300
dpi = 72.0
figsize = size[0] / float(dpi), size[1] / float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
plt.axes((0, 0.01, 1, 0.9), frameon=False)
for i, m in enumerate(markers):
marker(m, i)
plt.xlim(-0.2, 0.2 + 0.5 * n_markers)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# Store figure for use in reference sections.
glue("marker_styles_fig", fig, display=False)

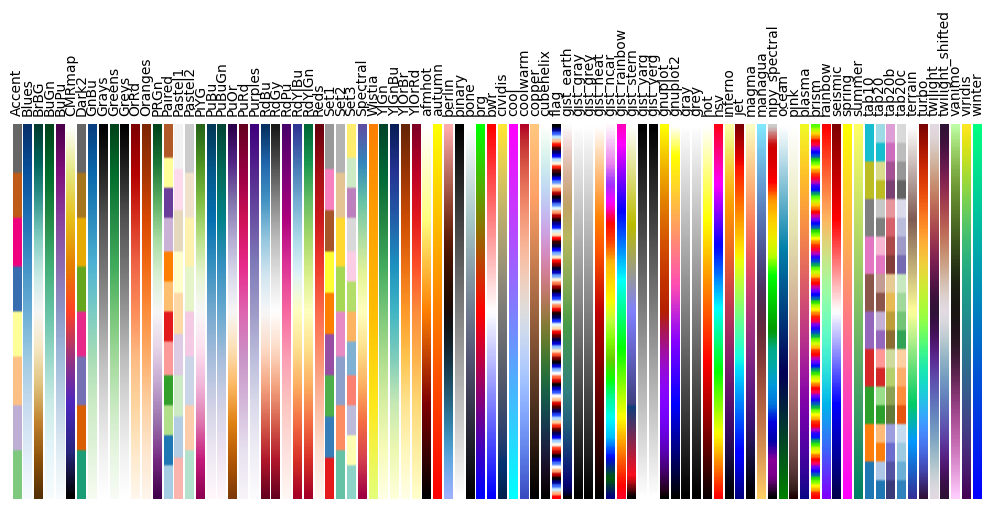
Colormap figure#
plt.rc("text", usetex=False)
a = np.outer(np.arange(0, 1, 0.01), np.ones(10))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.8, bottom=0.05, left=0.01, right=0.99)
maps = [m for m in plt.colormaps if not m.endswith("_r")]
maps.sort()
l = len(maps) + 1
for i, m in enumerate(maps):
plt.subplot(1, l, i + 1)
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(a, aspect="auto", cmap=plt.get_cmap(m), origin="lower")
plt.title(m, rotation=90, fontsize=10, va="bottom")
# Restore Matplotlib defaults.
plt.rcdefaults()
# Store figure for use in reference sections.
glue("colormap_fig", fig, display=False)